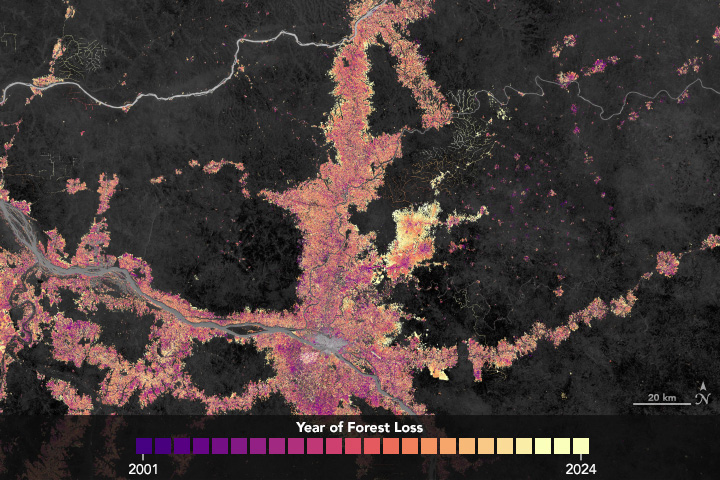
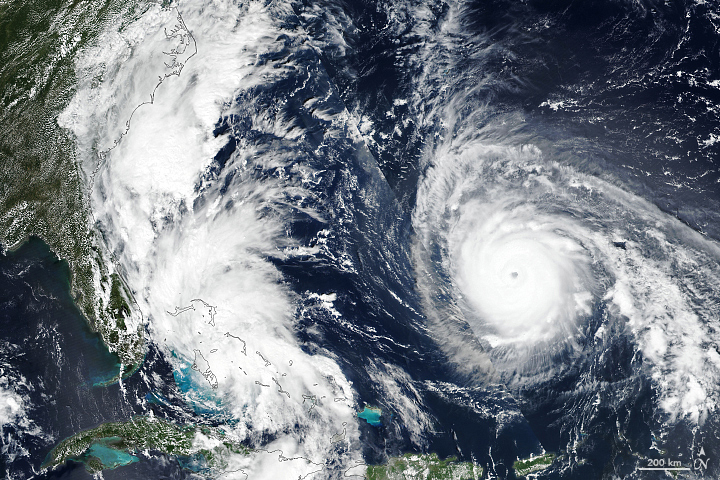



Recent Imagery
You will be directed to the NASA Visible Earth webpage when you select Images by Mission below, or click on the images at right that are randomly generated to represent four out of all possible topics.
You are here
Science Writers' Guide
NASA's Earth Observing System provides a variety of materials available for download. Feel free to choose a category below:
- Brochures
- Postcards
- Posters
- Science Writers’ Guide
- Mission Brochures
- Fact Sheets
- Calendars
- Booklets
- Lithographs
- Reference and Data Products Handbooks
- iBooks
- Activities
 |
CALIPSO/CloudSat/GRACE This publication is intended to be a one-stop resource for science writers and reporters who want to write about any of these three missions. For each satellite, the guide includes a quick reference sheet, Q&A, basics on the science of each mission, public affairs and scientist contact information, explanations of the satellites and their instruments, Web sites and other resources. This is related to the following mission(s):
This publication appears in:
|
 |
Aura NASA’s Earth Observing System (EOS) Aura satellite is a NASA mission whose purpose is to study the Earth’s ozone, air quality and climate. This mission is designed specifically to conduct research on the composition, chemistry and dynamics of the Earth’s upper and lower atmosphere employing multiple instruments on a single satellite. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
Aqua The launch of NASA’s Aqua spacecraft continued the Earth Observing System (EOS) series of comprehensive satellites to monitor the Earth from a space-based platform. Aqua was so named because it obtains significant information about water in the Earth system including ocean surface water, humidity, precipitation infiltration, and runoff. Data from six Aqua instruments provide continuous, long-term records of the hydrologic cycle around the world, which are combined with data from other Earth-monitoring satellites launched by NASA and other countries. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
SORCE SORCE, launched in March 2003, aims to enable solar-terrestrial studies by providing precise daily measurements of the Total Solar Irradiance and the Spectral Solar Irradiance at wavelengths extending from the ultraviolet to the near infrared. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
Landsat 7 The flagship EOS satellite, Terra (formerly EOS AM-1), launched in July 1999, is providing key measurements of the physical and radiative properties of clouds; air-land and air-sea exchanges of energy, carbon, and water; trace gases; and volcanoes. Flying in formation with Terra, Landsat 7 is making global high spatial resolution measurements of land surface and surrounding coastal regions. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
Terra The launch of NASA’s Terra spacecraft in 1999, marked a new era of comprehensive monitoring of the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and continents from a single space-based platform. Data from the five Terra instruments are creating continuous, long-term records of the state of the land, oceans, and atmosphere. Together with data from other satellite systems launched by NASA and other countries, Terra inaugurated a new 15-year data record. This is related to the following mission(s): This publication appears in: |
 |
Ocean Surface Topography Mission/Jason-2 (2008) The Ocean Surface Topography Mission (OSTM)/Jason-2 advances our understanding of ocean circulation and will improve our ability to forecast climate events and measure global sea-level change. The instruments on board are designed to map ocean surface topography to provide information on ocean wave heights, sea surface topography, tides, and water vapor. OSTM/Jason-2 continues the tasks of the Jason-1 mission. This publication appears in: |
